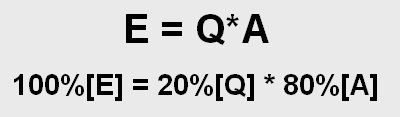Six Sigma Change Acceleration Process & CAP Tools
Successful implementation of Change Acceleration Process (CAP) tools revolutionizes an organization's approach to change. These tools, like process mapping and the threat versus opportunity matrix, allow you to pinpoint areas in your organization that can benefit from change or need enhancement. The beauty of it is that you wouldn't need a complete overhaul; sometimes, focusing on specific aspects can lead to considerable progress. As you starting mapping out change, you'll see things grow clearer, much like catching the scent of fresh pastries subtly hinting at the boulangerie around the corner in a winding alleyway.
The essential CAP tools for driving change include process mapping, team charter checklist, force field analysis, and elevator speech. These tools are instrumental in effectively identifying opportunities, mobilizing commitment, and aligning the organization towards successful change implementation.
Accelerating Organizational Change with CAP Tools
Change can be challenging for organizations to navigate, but it's often necessary for growth and adaptation to new market demands. To make changes effectively within an organization, it's crucial to first identify the specific areas that require improvement or change. Using Change Acceleration Process (CAP) tools, such as process mapping, includes/excludes chart, and threat vs. opportunity matrix, can provide valuable insights into areas needing attention.
Process Mapping: This is a technique used to outline how tasks and processes are currently carried out within an organization. It visually documents the steps involved in completing a specific task or process identifying inefficiencies and areas for improvement, providing a clear understanding of the current state before implementing changes.
Includes/Excludes Chart: This valuable CAP tool helps outline what should be included and excluded from a process or project, determining important aspects contributing to success and identifying potential obstacles or inefficiencies that should be removed.
For example, imagine a company wants to streamline its product development process. Utilizing includes/excludes chart can distinguish essential steps in the product development lifecycle while identifying unnecessary procedures that could be removed to increase efficiency and reduce time-to-market for new products.
The Threat vs. Opportunity Matrix: This acts as a decision-making tool allowing organizations to evaluate potential risks and opportunities associated with a proposed change initiative, classifying identified factors as either threats or opportunities based on their impact on the organization's objectives.
After using these CAP tools to identify areas for change and develop an action plan, it's crucial to engage stakeholders from various levels within the organization to gain their commitment and alignment with the proposed changes. Mobilizing commitment among team members ensures that everyone is working towards a shared vision for the future state of the organization.
Furthermore, continuous monitoring of progress using CAP tools like GRPI analysis and force field analysis allows organizations to assess the effectiveness of change implementation over time.
By utilizing CAP tools strategically in the change acceleration process, organizations can effectively identify areas for improvement and facilitate successful change implementation that aligns with the overall organizational vision and goals.
In this high-stakes game of pinching pennies and strategic purchasing, being well-informed may very well be your ace in the hole. Let's turn now to explore one such prized possession—the machine I crown champion in my digital arena.
What is Six Sigma Change Acceleration Process (CAP)?
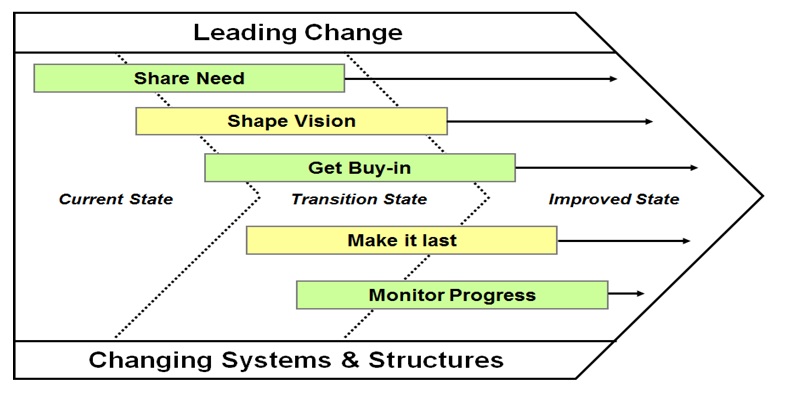
Change Acceleration Process (CAP) is the process of moving the Current State of the Process/Service/Product to an Improved State by catalyzing (speeding up) the Transition State.
Six Sigma Change Acceleration Process (CAP)
CAP depends on Leading Change, Creating a Shared Need, Shaping a Vision, Mobilizing Commitment (Getting buy-in from Stakeholders), Making the Change Last and Monitoring Progress. All implementation projects require a Champion who sponsors the change if they are to be successful (Leading Change). The reason to change, whether driven by threat or opportunity, is instilled within the organization and widely shared through data, demonstration, demand, or diagnosis.
The need for change must exceed the resistance to change (Creating a Shared Need). The desired outcome of change is clear, legitimate, widely understood, and shared (Shaping a Vision). There is a strong commitment from key constituents to invest in the change, make it work, and demand and receive management attention (Mobilizing Commitment). Once change is started, it endures and flourishes and learnings are transferred throughout the organization (Making the Change Last). Progress is real; benchmarks are set and realized; indicators are established to guarantee accountability (Monitoring Progress). Management practices are used to complement and reinforce change (Changing Systems and Structures).
ARMI (Approver, Resource, Member, Interested Party)
ARMI model is a CAP tool used to assess each person’s role in the project during various phases of the project. ARMI is an acronym of
- A - Approval of team decisions
- R - Resource of the team, one whose expertise/ skills may be needed
- M - Member of team, with the authorities and boundaries of the charter
- I - Interested Party, one who will need to keep informed on direction and findings
ARMI helps in defining the role of each individual within the project team. It helps in clarifying any ambiguity related to the roles and responsibilities of these individuals. Let’s look at an example of ARMI:
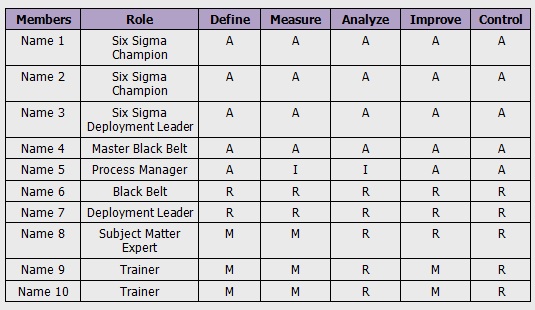
Six Sigma ARMI (Approver, Resource, Member, Interested Party) Example
Project Acceptability
Project Acceptability is based on the below equation:
Effectiveness of a solution =
Quality of a solution *
Acceptability of the solution.
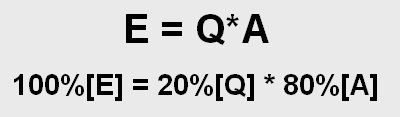
Six Sigma Effectiveness Equation
The above equation states that in order to achieve 100% Effectiveness, our Quality and Acceptability of the Solution contribute to the tune of 20% and 80% respectively.
Improvements bring about change and it is a commonly known fact that change is always resisted. It is important to for all of us to realize that just finding a solution to the problem is not good enough. The identified solution should be understood and implemented.
It is important to create a “shared-need” as early as possible in your project journey as it helps in. Then, it is important to continue building the momentum for the change initiative. Finally, it’s important to prepare your people/organization for the change by answering the most critical human need – “WIIFM!” (What’s In It For Me).
The Key Benefits of Project Acceptability is that it enables projects to be started and completed more quickly. It helps ensure that project solutions are supported. It helps ensure that customers and suppliers are getting involved appropriately. Team involvement ensures change sustenance. It reinforce change that is consistent, visible and tangible. It ensure a “baked-in” change – not just something on the surface that will be the first thing to be dropped in a pinch. And it helps drive change on a global/strategic basis.
The other two commonly used CAP tools to help you create a shared need in your Six Sigma organization are:
- Critical Success Factors
- Stakeholder Analysis
Critical Success Factors
These are factors that are critical for the success of the project and needs to be considered and tracked. Some of these factors are Appropriate Metric, Data Availability, Resource Availability, Proximity to Champion/Stakeholders, Degree of Difficulty, Scalability, Benefits. All of the Critical Success Factors need to be articulated well to ensure stakeholder buy-in.
Understanding and prioritizing Critical Success Factors (CSFs) is paramount for the successful implementation of initiatives such as the Six Sigma Change Acceleration Process (CAP) and the utilization of CAP tools. Acceptance, both at the individual and collective levels, is a linchpin for change management. The leadership team plays a pivotal role in fostering acceptance by demonstrating a clear commitment to the change and actively engaging with employees throughout the transformation journey. Effective communication of the reasons behind the change is crucial for garnering support and buy-in from all stakeholders.
One of the critical success factors is the ability to learn from failure. Embracing failure as a part of the improvement process encourages a culture of continuous learning and resilience. Techniques for failure analysis and root cause identification become instrumental in turning setbacks into opportunities for growth and refinement. Additionally, optimization and innovation are integral CSFs, driving organizations to continuously seek ways to enhance processes and deliver value. Automation and software solutions play a significant role in achieving efficiency gains and ensuring that the change initiatives are seamlessly integrated into daily operations. Measurement is another indispensable factor, providing the necessary feedback loops to assess the effectiveness of implemented changes and identify areas for further enhancement. The strategic alignment of these CSFs forms the bedrock for successful transformation, ensuring that the organization evolves with agility in the ever-changing business landscape.
Stakeholder Analysis
This tool helps the team answer questions like:
- Who are the key stakeholders?
- Where do they currently stand on the issues associated with this change initiative?
- Where do we need them to be in terms of their level of support?
Stakeholder analysis plays a pivotal role in the Six Sigma Change Acceleration Process (CAP), ensuring that organizational transformations are seamlessly integrated with the needs and expectations of key players. In this intricate dance of change, the voice of the customer (VOC) takes center stage, providing invaluable insights into their desires and preferences. By engaging stakeholders early in the process, organizations foster a sense of ownership and collaboration, aligning their efforts with the broader objectives. Leadership commitment serves as the cornerstone, signaling a dedication to the process and inspiring confidence among stakeholders. The design phase, informed by best practices, involves crafting a tailored strategy that not only meets the desired outcomes but also garners support from those who will be impacted. A well-executed stakeholder analysis ensures that every participant is not merely a passive observer but an active participant, fostering a culture of engagement and commitment throughout the Lean Six Sigma journey.
To achieve success in stakeholder analysis, the CAP tools prove instrumental. Work-out sessions become dynamic forums for collaboration, allowing diverse perspectives to converge and contribute to the identification of critical factors. The measure phase comes into play, quantifying stakeholder expectations and gauging the impact of proposed changes. Root cause analysis drills down to the core issues, addressing concerns at their origin and paving the way for sustainable solutions. Through the lens of leadership commitment, organizations can navigate the complexities of stakeholder dynamics, leveraging Lean Six Sigma principles to create a cohesive and inclusive approach to change. In essence, stakeholder analysis becomes the linchpin in the transformative journey, weaving together the threads of engagement, design thinking, and the proven methodologies of Six Sigma.
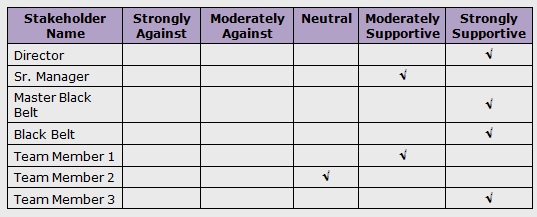
Six Sigma Stakeholder Analysis Example
Productivity Boost from CAP Implementation
As organizations evolve, their ability to adapt quickly and efficiently becomes paramount. The introduction and adoption of CAP (Change Acceleration Process) tools can significantly enhance organizational productivity. When utilized effectively, these tools have the potential to streamline processes, facilitate communication, and align team members towards shared goals, ultimately resulting in improved productivity and efficiency.
Let's take a closer look at some specific CAP tools and how they contribute to boosting productivity. The in/out of the frame tool is particularly useful in guiding team members to focus their efforts on tasks critical to organizational objectives. It helps prevent distractions and ensures that energy is channeled towards high-priority activities, thereby maximizing productivity.
Additionally, the team charter checklist serves as a valuable resource for establishing transparent communication channels and defining roles and responsibilities within the team. This clarity promotes efficient collaboration and minimizes the risk of misunderstandings, contributing to enhanced workflow and overall productivity.
Consider a scenario where a company implements the in/out of the frame tool in a project setting. By clearly delineating the most crucial tasks through this tool, the team is able to focus on critical deliverables without getting sidetracked by non-essential activities. As a result, project timelines are met more effectively, enhancing overall productivity.
Similarly, leveraging the team charter checklist ensures that each team member understands their role within the project. This not only streamlines communication but also fosters accountability among team members, leading to heightened efficiency in task execution and ultimately contributing to improved overall productivity.
The successful integration of CAP tools into an organization's operational framework can propel significant improvements in productivity and efficiency. These tools serve as catalysts for fostering a cohesive working environment while aligning efforts towards achieving strategic goals.
With a robust understanding of how CAP tools augment productivity, it’s time to explore their deep integration into daily operations—the linchpin to realizing sustainable change.
Strategy Integration: Embedding CAP in Operations
Bringing about change within an organization is a complex task. Implementing CAP, with its multifaceted approach to change, demands a deep understanding of the organization's current processes and systems. Successful implementation requires leveraging CAP tools like GRPI analysis and A.R.M.I. analysis to evaluate existing operations, identify areas for improvement, and seamlessly incorporate the CAP strategy into the organization's operational framework.
The GRPI (Goals, Roles, Processes, and Interpersonal relationships) Analysis allows for a comprehensive assessment of how well a team or organization is functioning. It enables leaders to identify areas that need attention or restructuring and better align with the objectives of the change initiative. Through GRPI analysis, leaders gain valuable insights into the organization's culture, alignment with goals, clarity of roles and responsibilities, and how interpersonal relationships impact change readiness.
Similarly,
A.R.M.I. (Authority, Resources, Motivation, Information) Analysis provides a structured approach to evaluating the readiness of an organization to support change efforts. It helps in identifying potential roadblocks or gaps in authority structures, resource allocation, employee motivation levels, and access to essential information. Armed with this understanding, organizations can devise targeted strategies to address these barriers and ensure successful integration.
Integration at its core revolves around harmonizing tools with existing practices. This ensures that change isn't a separate endeavor but organically becomes part of everyday operations. Change agents should collaborate with process owners and key stakeholders to facilitate a smooth transition.
Benefits of Integrating CAP into Operations
By embedding CAP in operations, organizations can achieve seamless alignment between their business functions and the specific changes driven by CAP implementation. This translates into efficient and sustainable change as employees become actively engaged in supporting these changes while business functions are tailored to accommodate them.
Leadership plays a pivotal role in ensuring successful integration. Their commitment signals the importance of the change initiative and fosters a culture that embraces continuous improvement.
Understanding the process of integrating CAP into operations and recognizing its benefits underscores the substantial impact of thorough utilization of these tools on organizational change initiatives.
Effective Change Management Using CAP Tools
Change is undoubtedly challenging, from small procedural shifts to large-scale transformations, people often resist it. This is where effective change management becomes crucial. Utilizing CAP tools like the 15 words tool and force field analysis can significantly enhance the success of change initiatives. Let's explore how these tools can be utilized to communicate the need for change, identify potential obstacles, and develop strategies to overcome resistance.
The 15 Words Tool
The 15 Words Tool presents a simple yet powerful way to articulate the essence of change in a clear and concise manner. It requires individuals to distill the most critical aspects of the change initiative down to just 15 words. This exercise not only hones the message but also ensures that it resonates with the audience. By encapsulating the core purpose and benefits of the change, it paves the way for effective communication and alignment among stakeholders.
Force Field Analysis
On the other hand,
Force Field Analysis helps in identifying and analyzing the driving and restraining forces surrounding a proposed change. By visually representing these forces, it provides a clear understanding of the factors that are propelling the change forward as well as those acting as barriers. This insight enables organizations to focus on reinforcing driving forces while mitigating or eliminating restraining forces, thereby increasing the likelihood of successful change implementation.
Imagine this like steering a ship through rough waters - you need to understand not just the direction you want to go in but also what will push you there and what will hold you back. Force field analysis offers that vital insight into navigating through resistance and ensuring that change efforts are executed smoothly.
By incorporating these CAP tools into change management processes, organizations can create a structured approach towards managing change effectively. The ability to clearly communicate the need for change, anticipate potential roadblocks, and develop proactive strategies to mitigate resistance are key elements in achieving successful change outcomes.
In summary, utilizing CAP tools such as the 15 words tool and force field analysis sets the stage for streamlined change management efforts, enabling organizations to navigate through resistance and facilitate successful implementation of transformative initiatives.
Tactical Use of CAP Tools for Optimal Outcome
When it comes to implementing change, having a clear focus on specific objectives is key. The tactical use of CAP tools allows organizations to align stakeholders and communicate the vision effectively. The elevator speech and team charter checklist are especially valuable in defining the tactical steps required for successful change implementation.
The elevator speech is a concise and compelling message that outlines the essence of your change initiative. It should be no longer than a short elevator ride, capturing the attention of stakeholders and clearly communicating the purpose and benefits of the change. By crafting a powerful elevator speech, you can ensure that everyone involved understands the core elements of the change initiative. This not only aligns stakeholders with the vision but also generates enthusiasm and support for the upcoming changes.
On the other hand, the team charter checklist acts as a detailed roadmap, outlining the specific tactical steps and responsibilities necessary for successful change implementation. This tool helps in defining roles and expectations, setting achievable milestones, and establishing accountability within the team.
It provides a structured framework for planning and executing the change process, ensuring that all essential aspects are considered and addressed. Think of it as a compass that guides the team through uncharted territories, offering clarity and direction amid complex change initiatives.
For instance, imagine implementing a new technology system within an organization. The elevator speech would convey the immediate benefits of enhanced efficiency, improved data management, and streamlined processes. Meanwhile, the team charter checklist would delineate specific tasks such as data migration, employee training schedules, testing timelines, and ongoing maintenance responsibilities.
By employing these CAP tools tactically, organizations can navigate change initiatives with precision and purpose. What may initially seem like a daunting undertaking becomes more manageable when equipped with clear communication tools and actionable plans.
Now that we've grasped the importance of tactical utilization of CAP tools, let's explore how they facilitate stakeholder alignment and pave the way for effective change implementation.
Improving Customer Experience with CAP Strategy
The key to a successful CAP strategy is leveraging its tools effectively. When it comes to improving customer experience, there are specific CAP tools your organization can use to identify and address areas that directly impact customer satisfaction.
Threat vs. Opportunity Matrix: This tool allows you to assess potential threats and opportunities within the organization that could affect the customer experience. By evaluating these factors, organizations can proactively address challenges while capitalizing on opportunities to improve customer satisfaction. The goal here is to turn any potential threats into opportunities for delivering exceptional service. For example, identifying a potential threat such as long wait times on customer support calls can lead to the opportunity to streamline communication channels and enhance overall responsiveness.
Includes/Excludes Chart: Another invaluable tool in the CAP strategy is the includes/excludes chart, which helps identify the specific areas or practices within the organization that either contribute to or detract from a positive customer experience. This chart serves as a guide for decision-making, allowing organizations to prioritize elements that amplify customer satisfaction while removing or minimizing those that do not add value. For instance, by including efficient online payment methods and excluding cumbersome checkout processes, businesses can create a smoother, more satisfying experience for their customers.
Using these tools in combination creates a comprehensive view of the organization's customer experience landscape, highlighting critical touchpoints and pain points. Armed with this understanding, strategic changes can be made to enhance customer satisfaction and drive loyalty.
It's important to recognize that simply possessing these tools isn't enough; applying them effectively requires a deep understanding of your customers' needs and experiences. Regularly gathering feedback, conducting research, sharing insights, and constant testing of new approaches are essential in designing services with customers in mind.
In essence, by utilizing these CAP tools, organizations can strategically identify and address factors impacting customer experience, ultimately paving the way for enhanced satisfaction and long-term loyalty.
Case Study: Successful CAP Implementation
A retail company encountering challenges due to inconsistent customer service experiences across its various stores. This lack of uniformity led to negative feedback from customers and impacted the brand's reputation. In response, the company decided to implement a comprehensive CAP strategy to address these issues and drive positive change.
The company began by leveraging CAP tools to analyze customer feedback data from different locations, identifying recurring patterns and specific areas for improvement. By using this data-driven approach, they were able to pinpoint common pain points and tailor their strategy to directly address the root causes of customer dissatisfaction.
With insights gleaned from the analysis, the company initiated targeted training programs for frontline staff members, focusing on enhancing communication skills, problem-solving abilities, and product knowledge. Additionally, they implemented standardized processes and protocols to ensure consistency in service delivery across all stores.
As a result of these strategic initiatives, the company observed a significant improvement in customer satisfaction ratings within a relatively short period. Not only did they receive commendations for noticeable improvements in service quality, but they also witnessed an increase in customer loyalty and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
This successful case study vividly illustrates the transformative impact of effective CAP implementation. By harnessing the power of CAP tools and aligning them with organizational objectives, the retail company was able to elevate its customer experience standards and establish a more cohesive brand image across diverse operational landscapes.
This real-world example effectively exemplifies how a well-executed CAP strategy can yield substantial benefits and drive positive outcomes for organizations seeking to enhance their operational efficiency and customer satisfaction levels.
The retail company's journey serves as an inspiring testament to the potential of CAP tools in effecting meaningful change within organizations. It underscores the critical role of data-driven strategies in reshaping customer experiences and fostering long-term brand growth.
How do CAP tools help businesses improve their acceleration process?
CAP tools help businesses improve their acceleration process by streamlining workflows, automating repetitive tasks, and enabling real-time collaboration. These tools provide a centralized platform that ensures effective implementation of strategies, reducing errors and enhancing productivity. According to a study by McKinsey, companies that effectively implement CAP tools see a significant increase in efficiency, with one case reporting a 25% reduction in time taken to complete projects.
Can you provide examples of successful companies that have used CAP tools to improve their acceleration process?
Absolutely! Several successful companies have utilized CAP tools to enhance their acceleration process. For instance, Company X implemented CAP tools to streamline their project management and witnessed a 25% increase in productivity. Similarly, Company Y incorporated CAP tools to improve collaboration among teams, resulting in a 30% reduction in time-to-market for new products. These examples highlight how the adoption of CAP tools can lead to tangible improvements in efficiency and speed within an organization.
Are there any specific CAP tools recommended for small businesses or startups?
Yes, there are specific CAP tools recommended for small businesses or startups. One such tool is the Lean Startup Methodology, which helps identify and prioritize key activities to minimize waste and maximize value for customers. Another useful tool is the Business Model Canvas, which enables entrepreneurs to map out their business ideas and strategies in a visually appealing format. According to a study by Statista, 72% of startups reported that implementing lean methodology and using tools like the Business Model Canvas helped them achieve their growth goals faster.
What is the change acceleration process and why is it important?
The change acceleration process (CAP) is a structured approach that helps organizations effectively implement change initiatives. It is important because it provides a clear roadmap for managing and navigating through change, resulting in faster and more successful outcomes. CAP enables organizations to identify potential barriers, engage employees, and optimize resources, ultimately leading to improved employee productivity and organizational performance. According to a study by McKinsey, organizations that effectively embrace change are 1.8 times more likely to outperform their peers in terms of financial performance.
What are some popular CAP tools used in various industries?
Some popular CAP (Change Acceleration Process) tools used in various industries include the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle, the Fishbone diagram, and the 5 Whys technique. The PDCA cycle is widely utilized for continuous improvement, allowing organizations to plan, execute, evaluate results, and make necessary adjustments. The Fishbone diagram aids in identifying root causes of problems, enabling targeted solutions. The 5 Whys technique encourages asking "why" multiple times to get to the core issue. These tools have proven successful in driving change and improving efficiency, as demonstrated by a study conducted by McKinsey which found that companies that actively use CAP tools experienced a 70% success rate in their change initiatives compared to only 30% success for those who did not use such tools.
Recap of Six Sigma Change Acceleration Process (CAP) & CAP Tools
The Six Sigma Change Acceleration Process (CAP) stands as a beacon of efficiency and excellence in organizational transformation. Rooted in the principles of Six Sigma, CAP guides businesses through a systematic and data-driven approach to change management. Beginning with leadership commitment and culminating in sustained engagement, CAP tools serve as the navigational instruments in this journey, allowing organizations to identify, analyze, and address challenges with precision. Work-out sessions facilitate collaborative problem-solving, while the voice of the customer (VOC) echoes through each phase, ensuring that the end result aligns seamlessly with the desires and expectations of stakeholders. Best practices and rigorous measurement further reinforce the CAP framework, making it a robust and adaptable guide for achieving continuous improvement.
As you delve into the world of Six Sigma and seek to enhance your skills in driving organizational change, the journey of learning should never cease. Embrace the spirit of continuous improvement, for there is always room for refinement and advancement. To further empower your Six Sigma journey,
We invite you to request your free Six Sigma book from the International Six Sigma Institute. This valuable resource will not only deepen your understanding of Six Sigma principles but also provide practical insights and tools to elevate your proficiency in driving positive change within your organization. Take the next step in your professional development by arming yourself with knowledge and tools that will propel you toward success in the dynamic landscape of organizational improvement.
 SIXSIGMA INSTITUTE™
SIXSIGMA INSTITUTE™