What is Six Sigma Methodology?
Detailed Guide to the Six Sigma Process
Six Sigma is a defined and disciplined business methodology to increase customer satisfaction and profitability by streamlining operations, improving quality and eliminating defects in every organization-wide process.
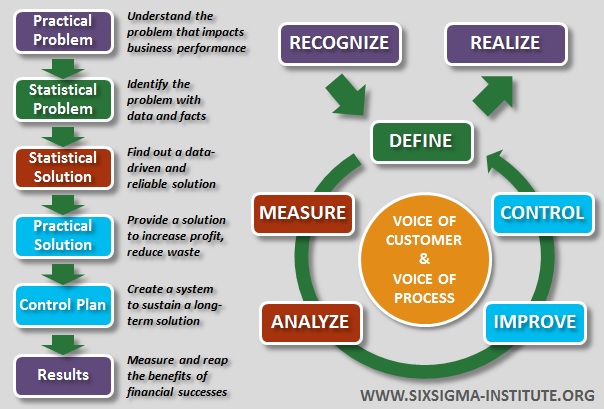
Six Sigma Methodology is a powerful tool for enhancing the quality of goods and services. It's founded on making data-driven decisions to reduce defects and heighten efficiency. A key part of this technique involves using a step-by-step method known as DMAIC, short for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control, which helps in eradicating errors systematically. Exploring these concepts more closely will change your perspective on managing processes. Let's start by understanding their core principles.
Six Sigma and DMAIC Methodology Overview
The key principles of the Six Sigma methodology include process improvement, reduction of variation, data-driven decision-making, and a focus on achieving 3.4 defects per million opportunities. By following the DMAIC approach (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) and utilizing statistical tools, organizations can systematically improve their processes and enhance overall quality.
What is Six Sigma?
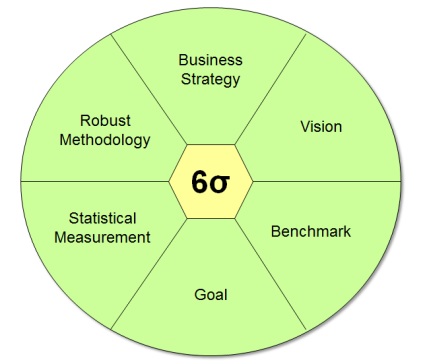
Six Sigma is:
- A Business Strategy: Using Six Sigma Methodology, a business can strategize its plan of action and drive revenue increase, cost reduction and process improvements in all parts of the organization.
- A Vision: Six Sigma Methodology helps the Senior Management create a vision to provide defect free, positive environment to the organization.
- A Benchmark: Six Sigma Methodology helps in improving process metrics. Once the improved process metrics achieve stability; we can use Six Sigma methodology again to improve the newly stabilized process metrics. For example: The Cycle Time of Pizza Delivery is improved from 60 minutes to 45 minutes in a Pizza Delivery process by using Six Sigma methodology. Once the Pizza Delivery process stabilizes at 45 minutes, we could carry out another Six Sigma project to improve its cycle time from 45 minutes to 30 minutes. Thus, it is a benchmark.
- A Goal: Using Six Sigma methodology, organizations can keep a stringent goal for themselves and work towards achieving them during the course of the year. Right use of the methodology often leads these organizations to achieve these goals.
- A Statistical Measure: Six Sigma is a data driven methodology. Statistical Analysis is used to identify root-causes of the problem. Additionally, Six Sigma methodology calculates the process performance using its own unit known as Sigma unit.
- A Robust Methodology: Six Sigma is the only methodology available in the market today which is a documented methodology for problem solving. If used in the right manner, Six Sigma improvements are bullet-proof and they give high yielding returns.
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma Methodology Fundamentals
At the heart of Six Sigma lies a commitment to continuous improvement, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. The
DMAIC framework—Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control—serves as a roadmap guiding organizations toward their quality and efficiency objectives. Let's explore the core concepts and principles that underpin this systematic approach.
First off, Six Sigma emphasizes the importance of defining customer requirements with precise clarity. Before embarking on any process improvement initiative, it’s vital to comprehend what customers value and expect from the products or services being delivered. Meeting these requirements is essential for customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Moving on to measurement, Six Sigma requires a deep understanding of current process performance through rigorous data collection and analysis. This involves quantifying the number of defects or errors in a process—enabling organizations to establish a baseline for improvement initiatives. Without accurate measurement, it’s impossible to identify areas for enhancement.
The analysis phase digs deeper into the root causes of defects or inefficiencies within the process. Armed with comprehensive data, organizations can pinpoint bottlenecks, waste, or variations that impede the achievement of desired outcomes. By understanding why problems occur, solutions can be tailored to address the specific issues at hand.
This brings us to improvement—the “I” in
DMAIC—where interventions are identified and applied to drive positive change in the process. Implementing solutions derived from thorough analysis aims to significantly enhance the overall performance, quality, and efficiency of the process.
Finally, we arrive at control—the stage where sustained success is secured by establishing mechanisms to monitor performance. Implementation of standardized procedures ensures that improvements are maintained over time and prevents regression back to previous inefficiencies.
Understanding these foundational concepts and principles of Six Sigma equips organizations with the knowledge required for successful implementation—laying the groundwork for enhanced process quality, customer satisfaction, and ultimately driving business success.
With a solid understanding of the fundamental aspects of Six Sigma methodology, let's now shift our focus to examining the practical application of these principles in the realm of Process Management and Improvement.
Process Management and Improvement
Optimizing business processes lies at the core of Six Sigma. It's about ensuring that the journey from point A to B is as smooth as possible and that every step is efficient and effective. Start by identifying the key processes that directly impact product quality, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency. For instance, in manufacturing, this might be the production process, while in the service industry, it could be the customer service or support process.
When identifying key processes, consider those with a significant influence on your business objectives. Focusing on these areas allows you to prioritize efforts and allocate resources effectively. This targeted approach not only streamlines process improvement initiatives but also maximizes their impact.
Mapping and Analyzing Processes
Once key processes are identified, it's time to map and analyze them. Process mapping visualizes each step in a process, making it easier to understand how activities are connected and pinpoint potential areas for improvement. Tools like flowcharts and process maps provide a clear overview of how processes currently operate and highlight any bottlenecks or inefficiencies.
For example, when examining the order fulfillment process in a retail company, mapping each stage from order placement to delivery allows for spotting common areas of delay or error. This visualization enables targeting specific points for improvement.
With this visual representation, you can analyze processes more effectively. Look for redundant steps, unnecessary handoffs between teams, or any other inefficiencies impacting the overall process. This detailed analysis forms the basis for informed decision-making regarding process improvement.
Implementing Process Changes
The ultimate goal of process management and improvement within Six Sigma is to implement changes leading to improved quality and efficiency. This doesn't involve minor tweaks; it requires a holistic rethinking of task execution. Applying Six Sigma principles such as DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) assists in redesigning processes to eliminate defects and enhance operational performance.
To illustrate, think of it as renovating an old house. It's not just about cosmetic changes; it's about fundamental alterations that create lasting positive impacts. When implementing process changes, involving all stakeholders is crucial. Employees engaging with these processes hold valuable insights into practical improvements, while top management support ensures adequate resources are allocated for effective change driving.
In summary, process management and improvement in Six Sigma includes identifying key processes, thoroughly analyzing them for potential enhancement, and implementing strategic changes resulting in heightened quality and efficiency across all facets of operations.
Understanding the intricacies of process mapping sets the stage for a deep dive into Statistical Analysis in Six Sigma – an indispensable component of driving sustained quality improvements.

Six Sigma Methodology
Statistical Analysis in Six Sigma
Statistical analysis is the bedrock of Six Sigma, enabling experts to uncover patterns, identify anomalies, and make informed decisions based on data. By leveraging powerful tools and techniques, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of their processes and achieve greater consistency and efficiency.
One essential statistical tool used in Six Sigma is
hypothesis testing. This method allows teams to evaluate different hypotheses about a process to determine if there is a significant difference between two scenarios. For instance, it can help determine whether changes made to a manufacturing process have led to a noticeable improvement in product quality or if they had no effect at all.
Six Sigma also relies heavily on
regression analysis, which helps in understanding the relationship between variables and identifying which ones have a significant impact on process outcomes. By studying how changes in one variable correlate with changes in another, organizations can pinpoint which factors are most critical to process quality and efficiency.
Another fundamental statistical approach within Six Sigma is the use of
control charts. These charts monitor process performance over time, allowing teams to detect any deviations or trends that fall outside the expected range. This empowers them to take proactive measures to maintain consistency and prevent defects from occurring.
Moreover,
design of experiments (DOE) is a critical statistical technique often employed in Six Sigma projects. DOE enables organizations to systematically change multiple input variables to identify the best combination for achieving desired process outcomes. This method provides insights into optimal process settings while minimizing the impact of variability.
For instance, imagine a manufacturing company implementing Six Sigma principles to improve the reliability of its production line. By conducting regression analysis, they might discover that variations in temperature significantly affect the quality of their products. Using this insight, they then implement control charts to closely monitor temperature fluctuations and identify potential issues before they impact product quality.
By integrating these statistical methods into their improvement initiatives, organizations can precisely understand how various factors affect their processes' performance and output quality. Additionally, they empower teams to make informed decisions based on credible data rather than relying on assumptions or guesswork.
The application of statistical analysis in Six Sigma methodologies serves as a linchpin for driving continuous improvement initiatives and enhancing overall operational effectiveness.
As we shift our focus towards achieving excellence through precision and measurement, let's explore the realm of "Effective Measurement Systems".
Effective Measurement Systems
Effective measurement systems are the backbone of any successful process improvement initiative. They provide crucial insights into process performance and quality, enabling organizations to make informed decisions and drive continuous improvement. Let's break down the key components of implementing effective measurement systems in Six Sigma.
Defining Key Metrics
In the world of Six Sigma, defining key metrics is akin to identifying the compass that guides your journey towards process excellence. These metrics are vital signposts, pointing to areas where improvements are needed and indicating the success of implemented changes.
Critical process metrics should be carefully chosen to reflect the most impactful aspects of your business processes. For instance, in a manufacturing setting, key metrics might include defect rates, production cycle time, and equipment downtime. Conversely, in a service-oriented environment, customer satisfaction scores, response time, and error rates could be pivotal metrics.
It's not just about choosing any metric; it's about identifying those that have a direct impact on the quality and efficiency of your processes. These metrics need to be aligned with organizational goals and customer expectations. This ensures that efforts are focused on areas that will yield the most significant improvements.
Data Collection and Analysis
Once the key metrics are defined, it's time to roll up our sleeves and start collecting data. This isn't just any data collection; it's about gathering accurate and reliable information that provides a true reflection of process performance.
Data collected should be factual and verifiable, ensuring that the decisions made based on this data are well-informed. In Six Sigma, data analysis is a cornerstone activity. Through statistical tools and methods, organizations derive actionable insights from the collected data. This isn't about making wild guesses or assumptions; it's about using concrete evidence to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies within the business processes.
For example, let's consider a scenario where a business aims to reduce defects in its manufacturing line. The data collected might include defect counts at various stages of production, alongside associated process variables. By subjecting this data to statistical analysis techniques such as regression analysis or hypothesis testing, teams can identify root causes of defects and areas for improvement.
By leveraging data-driven insights obtained through rigorous analysis, organizations can pinpoint opportunities for process optimization and waste reduction.
Effective measurement systems form the bedrock of informed decision-making within Six Sigma methodology, providing organizations with the necessary visibility into their processes' performance and driving continuous improvement efforts.

Six Sigma Process
Incorporating Six Sigma Principles
When it comes to adopting Six Sigma principles within an organization, it's not just about implementing a new set of rules; it's about cultivating a philosophy of continuous improvement and quality excellence. This necessitates fostering a mindset where every employee in the organization is committed to making small changes that add up to significant improvement over time. The essence of Six Sigma lies in using data to drive decisions and focusing on meeting customer requirements.
But how can an organization start doing this?
First and foremost, training is crucial. Employees at all levels need to understand the Six Sigma methodologies and tools. From senior management to front-line workers, everyone should have a good grasp of how Six Sigma works and how they can contribute to its success. By investing in comprehensive training programs, organizations can ensure widespread adoption and active participation in process improvement initiatives.
In addition to training, it's important for leadership to consistently emphasize the importance of Six Sigma principles. When leaders actively communicate their support for the approach and align their decision-making processes accordingly, it sends a powerful message throughout the organization. This visible commitment from leadership helps establish a culture where everyone feels accountable for maintaining high standards and driving continuous improvement.
By incorporating these principles into everyday operations, organizations can create an environment where employees feel empowered to identify areas for improvement and take proactive steps to address them. This leads to a more agile, responsive, and customer-focused organization.
To truly embed Six Sigma principles into an organization's culture, it requires a concerted effort to champion these philosophies, provide accessible training, and lead by example at every level of the organizational hierarchy.
As organizations undergo the process of assimilating Six Sigma principles, the next crucial step involves deploying specific tools and strategies to bring these principles into action effectively.
Deployment of Six Sigma Tools
The deployment of Six Sigma tools is a critical step in the journey towards process improvement and quality management. It involves the strategic and systematic application of a set of powerful tools and techniques to drive measurable improvements in business processes. Let's take a closer look at some key tools used in Six Sigma methodology.
Use of Statistical Process Control (SPC)
One of the fundamental pillars of Six Sigma is the use of
Statistical Process Control (SPC) to monitor and control processes. SPC involves gathering and analyzing data to understand process performance, identify variations, and ensure that processes operate within established quality parameters. By using SPC techniques, organizations can gain insights into the stability and predictability of their processes, enabling them to make informed decisions based on statistical evidence.
Control Charts and Process Mapping
In addition to SPC, Six Sigma emphasizes the use of
control charts and process mapping as visual tools to represent process performance. Control charts provide a graphical representation of process data over time, allowing practitioners to identify patterns, trends, and variations that may indicate underlying process issues. Process mapping, on the other hand, involves creating visual representations of the steps and flow of a process, enabling a clear understanding of each stage and potential areas for improvement.
It's important for organizations to not only collect data but also analyze it effectively in order to drive process improvement.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Another vital tool in the Six Sigma toolkit is
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA). This proactive method is used to identify potential failure modes in processes or products, analyze their effects, and develop strategies to mitigate risks. Through FMEA, organizations can prioritize improvement efforts by focusing on critical processes or components that have the highest impact on product quality or customer satisfaction.
By proactively addressing potential failure modes, organizations can prevent defects before they occur.
The integrated approach offered by these tools plays a vital role in achieving significant enhancements in processes and products, ultimately driving business bottom-line by increasing profits and customer satisfaction. Combining these robust methods enables organizations to not only identify areas for improvement but also take concrete actions to enhance operational efficiency and deliver superior quality products or services.
For a more comprehensive understanding of applying Six Sigma principles and leveraging these tools effectively, consider exploring the resources available on our site. These resources offer in-depth insights, practical guidance, case studies, and examples to support your journey towards successful process improvement initiatives.
Frequently Asked Questions About Six Sigma Methodology
Can you provide examples of successful implementation of six sigma methodology?
Answer: Absolutely! Six Sigma has proven to be successful in various industries. For instance, General Electric (GE) successfully implemented Six Sigma and reported cost savings of over $32 billion between 1999 and 2024. Additionally, Motorola saw a reduction in product defects by 94% after adopting Six Sigma practices. These examples demonstrate the effectiveness of the methodology in driving process improvement, cost reduction, and quality management within organizations.
What industries typically use six sigma methodology?
Answer: Six Sigma methodology is widely used across various industries where process improvement and quality management are essential. Some of the industries that typically utilize six sigma include manufacturing, healthcare, finance, telecommunications, and retail. For instance, in manufacturing, six sigma has been proven to significantly reduce defects and improve productivity. In healthcare, it has helped hospitals improve patient satisfaction and decrease medical errors. Moreover, a study conducted by the American Society for Quality (ASQ) showed that organizations implementing six sigma reported an average cost savings of $290,000 per project.
How long does it typically take for an organization to fully adopt and implement six sigma methodology?
Answer: The time it takes for an organization to fully adopt and implement Six Sigma methodology can vary depending on several factors such as the size of the organization, the complexity of its processes, and the level of commitment from leadership. On average, it may take anywhere from 1 to 3 years for an organization to fully embrace and implement Six Sigma. According to a survey by International Six Sigma Institute, larger organizations with more than 10,000 employees took an average of 2.8 years to complete their Six Sigma journey while smaller organizations with less than 100 employees took an average of 1.7 years. It is important to note that successful implementation requires not only training and tools but also a cultural shift towards a data-driven and process-oriented mindset throughout the entire organization.
Are there any drawbacks or limitations to using six sigma methodology?
Answer: While Six Sigma methodology has proven to be highly effective in improving processes and quality management, there are a few drawbacks and limitations to consider. Firstly, the extensive data collection and analysis required can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Additionally, its strict adherence to statistical methods may not always be suitable for every situation or organization, particularly smaller ones. Finally, implementing Six Sigma may face resistance from employees who may perceive it as overly bureaucratic or disruptive to their established routines. According to research by Bain & Company, around 60% of companies that attempted to implement Six Sigma did not achieve the desired results or abandoned the initiative altogether.
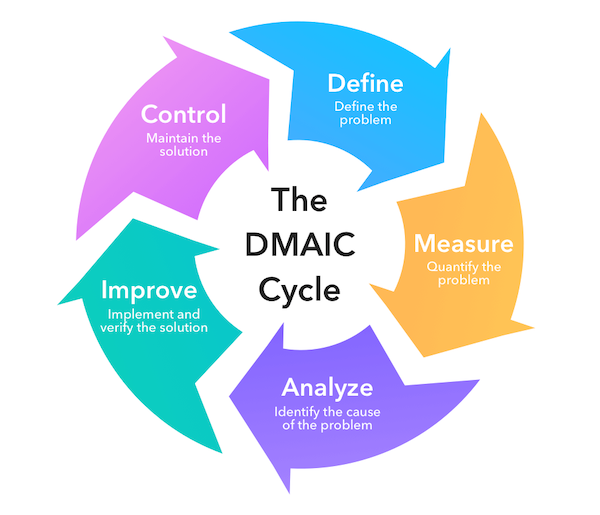
DMAIC Methodolody
What are the key principles and tools used in six sigma methodology?
Answer: The key principles of Six Sigma methodology include defining, measuring, analyzing, improving, and controlling processes. These principles are supported by various tools such as DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control), which provides a structured framework for process improvement. Additionally, statistical tools like process mapping, Pareto charts, and control charts are used to analyze data and identify root causes of defects or variations. According to a study by International Six Sigma Institute, companies implementing Six Sigma experienced an average cost savings of $174,000 per project and a 70% increase in customer satisfaction.
What are the benefits of implementing the six sigma methodology?
Answer: Implementing the Six Sigma methodology yields numerous benefits across organizations. By employing statistical tools and techniques, Six Sigma enhances decision-making, ensuring data-driven improvements in processes. The model emphasizes collaboration, fostering a team-oriented approach where individuals, often designated by "belts," work collectively to streamline operations. This systematic way of problem-solving not only enhances efficiency but also empowers people within the organization, promoting a culture of continuous improvement and long-term success.
What industries commonly use the six sigma methodology?
Answer: The Six Sigma methodology, with its roots in statistical principles and a defined set of phases, finds widespread application across various industries. Its primary goal is the standardization of processes to minimize defects and enhance efficiency. Businesses in manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and technology commonly employ Six Sigma to address root causes of issues, reduce costs, and meet the evolving needs of customers. Professionals in roles ranging from project managers to quality assurance experts play pivotal roles in implementing Six Sigma, overcoming challenges through data-driven analysis and strategic improvements with suppliers being integrated in ways that align with the methodology's principles.
Who should be involved in the implementation of the six sigma methodology within an organization?
Answer: Implementing the Six Sigma methodology within an organization requires a collaborative effort involving various stakeholders. Key participants should include top management, who play a pivotal role in establishing the program's infrastructure and ensuring alignment with organizational goals. Additionally, employees with expertise in statistics and root cause analysis are crucial for applying data-driven approaches and analyzing standard deviations to identify root causes. This inclusive approach ensures a comprehensive integration of the Six Sigma concept, leveraging its features to drive continuous improvement throughout the organization.
Where can I find online training courses for six sigma methodology?
Answer: For individuals seeking online training courses in Six Sigma methodology and aiming to obtain Six Sigma certifications, the International Six Sigma Institute offers comprehensive programs. Interested individuals can
Register on their website to access a range of certification options tailored to different levels of expertise. The institute's certification programs provide a structured and recognized pathway for professionals looking to enhance their skills in Six Sigma methodologies.
Where can I find books or literature on advanced concepts of six sigma methodology?
Answer: To delve into advanced concepts of Six Sigma methodology, one can explore a plethora of literature available in reputable libraries, online bookstores, and educational institutions offering courses on quality management. Valuable resources often cover topics such as statistical quality control, standard deviation analysis, and the intricacies of process improvement. Additionally, individuals keen on acquiring in-depth knowledge may benefit from the International Six Sigma Institute's certification program, and they can further enhance their understanding by
Requesting a complimentary Six Sigma Framework training book from the institute, fostering a comprehensive grasp of advanced Six Sigma principles.
What is the difference between Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma?
Answer: Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma are not distinct methodologies; rather, they are synonymous terms representing the identical process improvement approach. While some practitioners may use the term Six Sigma and others Lean Six Sigma, it is important to dispel any misconception of them being different. Six Sigma, originally developed as a process improvement method, seamlessly integrated principles from the Lean movement. Thus, whether referred to as Six Sigma or Lean Six Sigma, both labels unequivocally signify the same comprehensive methodology aimed at achieving operational excellence through meticulous process analysis and continuous improvement.
Six Sigma Methodology Recap
In summary, Six Sigma methodology is a robust and data-driven approach designed to enhance process efficiency and minimize defects. Its core principles include defining, measuring, analyzing, improving, and controlling processes, providing organizations with a structured framework for continuous improvement. By focusing on statistical methods and strategic problem-solving, Six Sigma aims to achieve excellence in operations and customer satisfaction.
For those keen on delving deeper into the world of Six Sigma, the journey does not end here. Continuous learning is pivotal to mastering this methodology and applying it effectively in various contexts. Whether you're a seasoned professional or new to Six Sigma, there is always room for expanding your knowledge and refining your skills. To take your understanding of Six Sigma to the next level, we encourage you to
Request a free copy of the Six Sigma Framework book from the International Six Sigma Institute. This valuable resource serves as a comprehensive guide, providing insights and tools to empower individuals on their Six Sigma journey. Don't miss this opportunity to deepen your expertise and contribute to the success of your organization.
 SIXSIGMA INSTITUTE™
SIXSIGMA INSTITUTE™